Multi-User Mobile Augmented Reality for Cardiovascular Surgical Planning
Pratham Darrpan Mehta - Georgia Tech, Atlanta, United States
Rahul Ozhur Narayanan - Georgia Tech, Atlanta, United States
Harsha Karanth - Georgia Tech, Atlanta, United States
Haoyang Yang - Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, United States
Timothy C Slesnick - Emory University, Atlanta, United States
Fawwaz Shaw - Emory University/Children's Healthcare of Atlanta, Atlanta, United States
Duen Horng (Polo) Chau - Georgia Tech, Atlanta, United States
Screen-reader Accessible PDF
Download preprint PDF
Download Supplemental Material
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-16T16:54:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T16:54:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Augmented Reality, Mobile Collaboration, Surgical Planning
Abstract
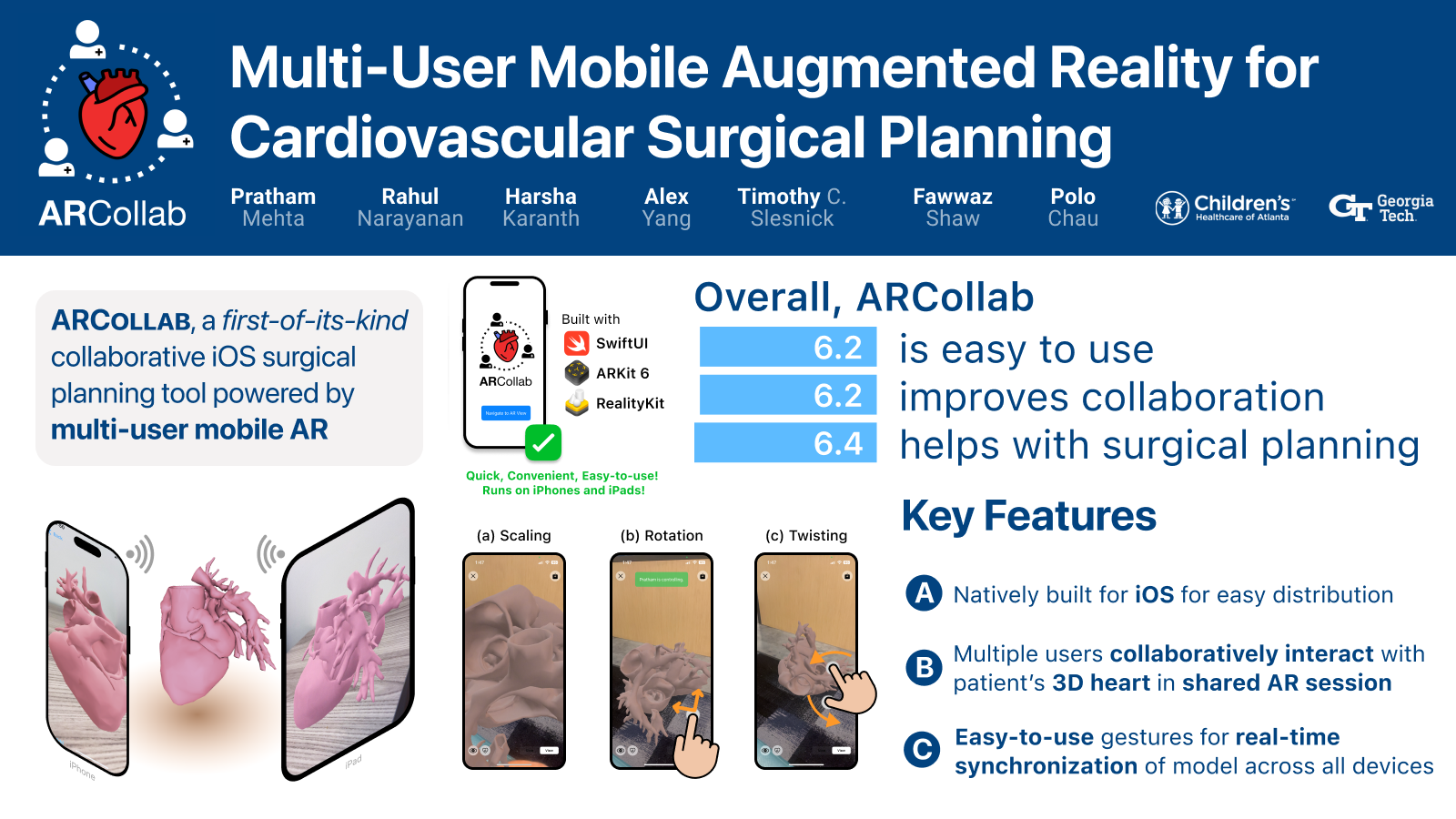
Collaborative planning for congenital heart diseases typically involves creating physical heart models through 3D printing, which are then examined by both surgeons and cardiologists. Recent developments in mobile augmented reality (AR) technologies have presented a viable alternative, known for their ease of use and portability. However, there is still a lack of research examining the utilization of multi-user mobile AR environments to support collaborative planning for cardiovascular surgeries. We created ARCollab, an iOS AR app designed for enabling multiple surgeons and cardiologists to interact with a patient's 3D heart model in a shared environment. ARCollab enables surgeons and cardiologists to import heart models, manipulate them through gestures and collaborate with other users, eliminating the need for fabricating physical heart models. Our evaluation of ARCollab's usability and usefulnessin enhancing collaboration, conducted with three cardiothoracic surgeons and two cardiologists, marks the first human evaluation of a multi-user mobile AR tool for surgical planning. ARCollab is open-source, available at https://github.com/poloclub/arcollab.