GhostUMAP: Measuring Pointwise Instability in Dimensionality Reduction
Myeongwon Jung - Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of
Takanori Fujiwara - Linköping University, Norrköping, Sweden
Jaemin Jo - Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of
Screen-reader Accessible PDF
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-16T13:24:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T13:24:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract
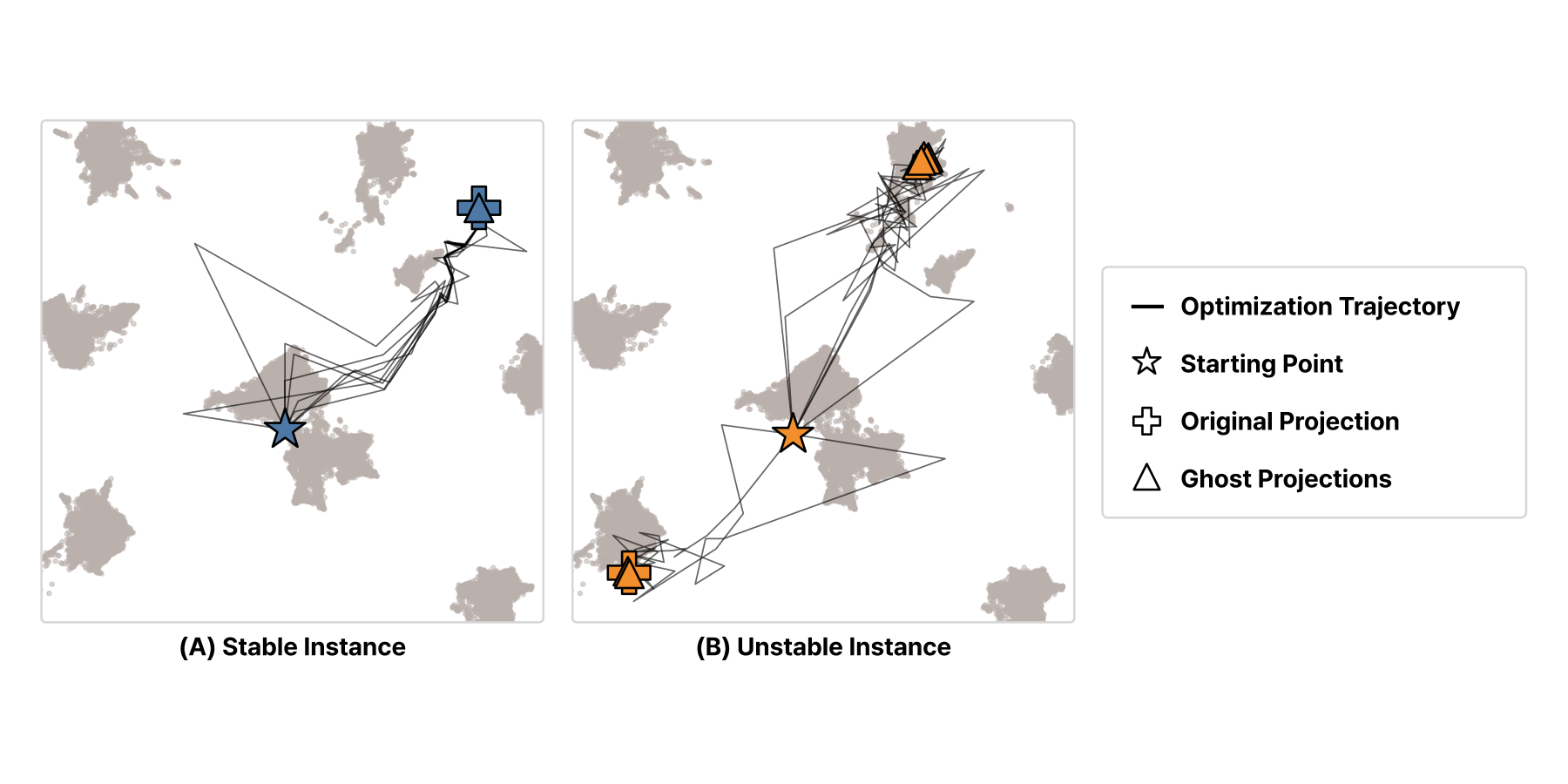
Although many dimensionality reduction (DR) techniques employ stochastic methods for computational efficiency, such as negative sampling or stochastic gradient descent, their impact on the projection has been underexplored. In this work, we investigate how such stochasticity affects the stability of projections and present a novel DR technique, GhostUMAP, to measure the pointwise instability of projections. Our idea is to introduce clones of data points, “ghosts”, into UMAP’s layout optimization process. Ghosts are designed to be completely passive: they do not affect any others but are influenced by attractive and repulsive forces from the original data points. After a single optimization run, GhostUMAP can capture the projection instability of data points by measuring the variance with the projected positions of their ghosts. We also present a successive halving technique to reduce the computation of GhostUMAP. Our results suggest that GhostUMAP can reveal unstable data points with a reasonable computational overhead.