ModalChorus: Visual Probing and Alignment of Multi-modal Embeddings via Modal Fusion Map
Yilin Ye - The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, China
Shishi Xiao - The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology(Guangzhou), Guangzhou, China
Xingchen Zeng - the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, China
Wei Zeng - The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, China. The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong SAR, China
Download preprint PDF
Room: Bayshore I
2024-10-17T12:54:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-17T12:54:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Multi-modal embeddings, dimensionality reduction, data fusion, interactive alignment
Abstract
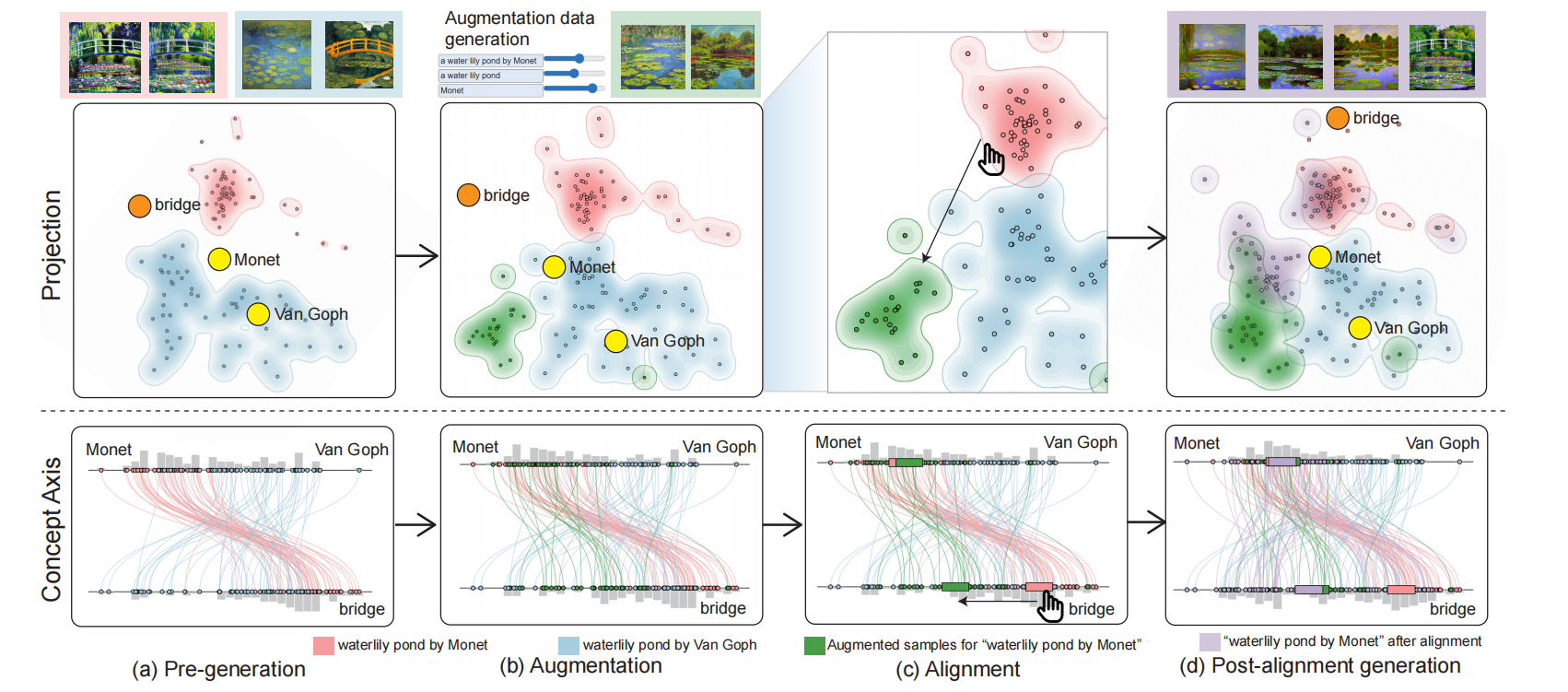
Multi-modal embeddings form the foundation for vision-language models, such as CLIP embeddings, the most widely used text-image embeddings. However, these embeddings are vulnerable to subtle misalignment of cross-modal features, resulting in decreased model performance and diminished generalization. To address this problem, we design ModalChorus, an interactive system for visual probing and alignment of multi-modal embeddings. ModalChorus primarily offers a two-stage process: 1) embedding probing with Modal Fusion Map (MFM), a novel parametric dimensionality reduction method that integrates both metric and nonmetric objectives to enhance modality fusion; and 2) embedding alignment that allows users to interactively articulate intentions for both point-set and set-set alignments. Quantitative and qualitative comparisons for CLIP embeddings with existing dimensionality reduction (e.g., t-SNE and MDS) and data fusion (e.g., data context map) methods demonstrate the advantages of MFM in showcasing cross-modal features over common vision-language datasets. Case studies reveal that ModalChorus can facilitate intuitive discovery of misalignment and efficient re-alignment in scenarios ranging from zero-shot classification to cross-modal retrieval and generation.