An Interactive Knowledge and Learning Environment in Smart Foodsheds
Yamei Tu -
Xiaoqi Wang -
Rui Qiu -
Han-Wei Shen -
Michelle Miller -
Jinmeng Rao -
Song Gao -
Patrick R. Huber -
Allan D. Hollander -
Matthew Lange -
Christian R. Garcia -
Joe Stubbs -
Screen-reader Accessible PDF
Download preprint PDF
Access paper PDF
DOI: 10.1109/MCG.2023.3263960
Room: Bayshore III
2024-10-16T16:36:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T16:36:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Learning Environment, Interactive Learning Environments, Programming Language, Visual System, Analysis Pipeline, Patterns In Data, Flow Data, Human-computer Interaction, Food Systems, Information Retrieval, Domain Experts, Language Model, Automatic Generation, Interactive Exploration, Cyberinfrastructure, Pre-trained Language Models, Resource Description Framework, SPARQL Query, DBpedia, Entity Types, Data Visualization, Resilience Analysis, Load Data, Query Results, Supply Chain, Network Flow
Abstract
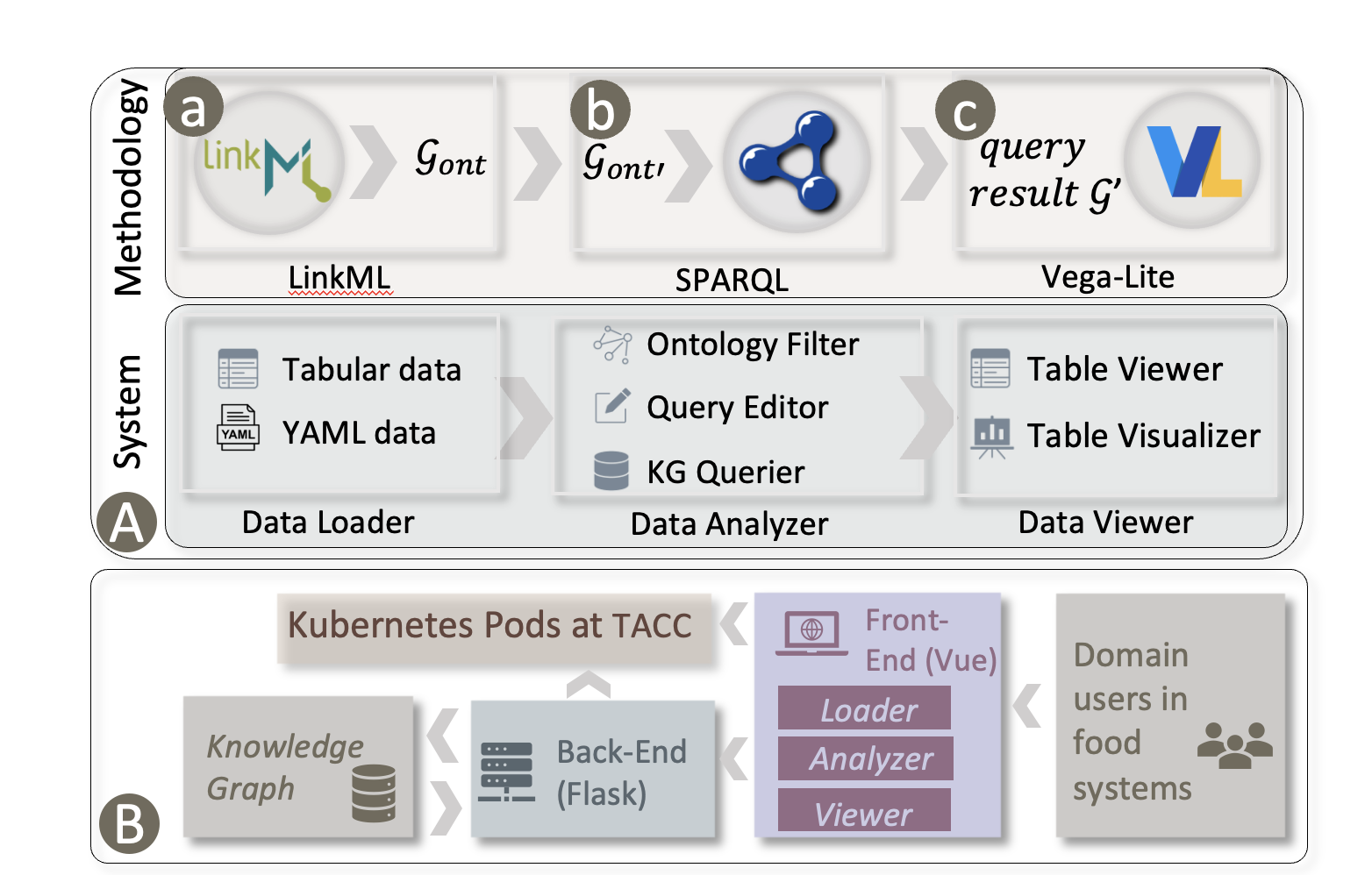
The Internet of Food (IoF) is an emerging field in smart foodsheds, involving the creation of a knowledge graph (KG) about the environment, agriculture, food, diet, and health. However, the heterogeneity and size of the KG present challenges for downstream tasks, such as information retrieval and interactive exploration. To address those challenges, we propose an interactive knowledge and learning environment (IKLE) that integrates three programming and modeling languages to support multiple downstream tasks in the analysis pipeline. To make IKLE easier to use, we have developed algorithms to automate the generation of each language. In addition, we collaborated with domain experts to design and develop a dataflow visualization system, which embeds the automatic language generations into components and allows users to build their analysis pipeline by dragging and connecting components of interest. We have demonstrated the effectiveness of IKLE through three real-world case studies in smart foodsheds.